Summary:
This clinical pocket guide serves as a comprehensive resource for healthcare professionals, particularly neonatal specialists seeking to harness the potential of transcutaneous CO2 monitoring in the care in the NICU. Providing a detailed overview of the clinical use cases, patient-specific considerations, and guidelines for application and use, it equips care teams with the knowledge necessary for successful transcutaneous CO2 monitoring.
Contents:
Importance of Gas Exchange in Neonates
Carbon Dioxide Management
Methods of Carbon Dioxide Monitoring
Principles of Operation and Equipment
Correlation with Arterial Blood Gas (ABG)
Clinical Use Cases
Reducing Iatrogenic Blood Loss
Continuous Monitoring, Titration, and Weaning of Mechanical Ventilation Support
Continuous Monitoring for High Frequency Ventilation (HFV)
Reducing Neonatal Pain and Stimulation
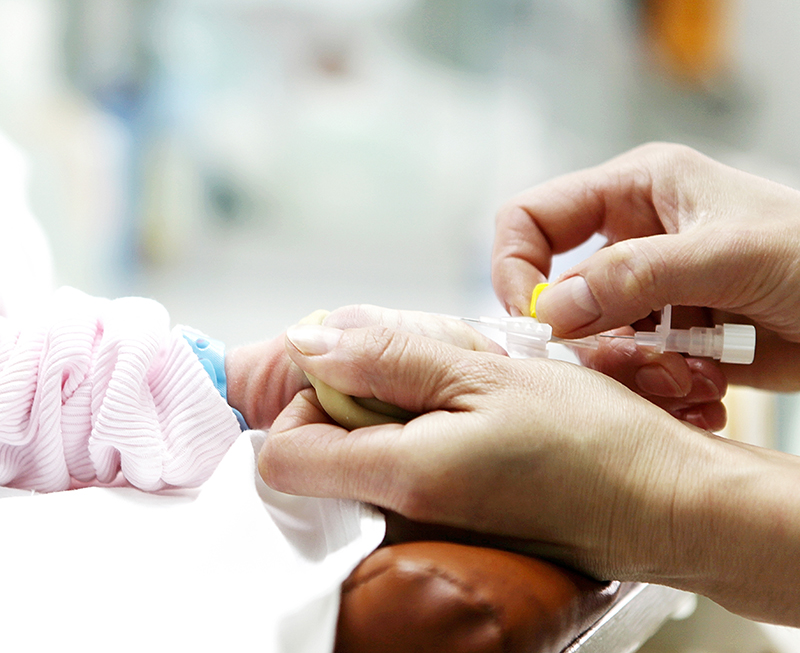
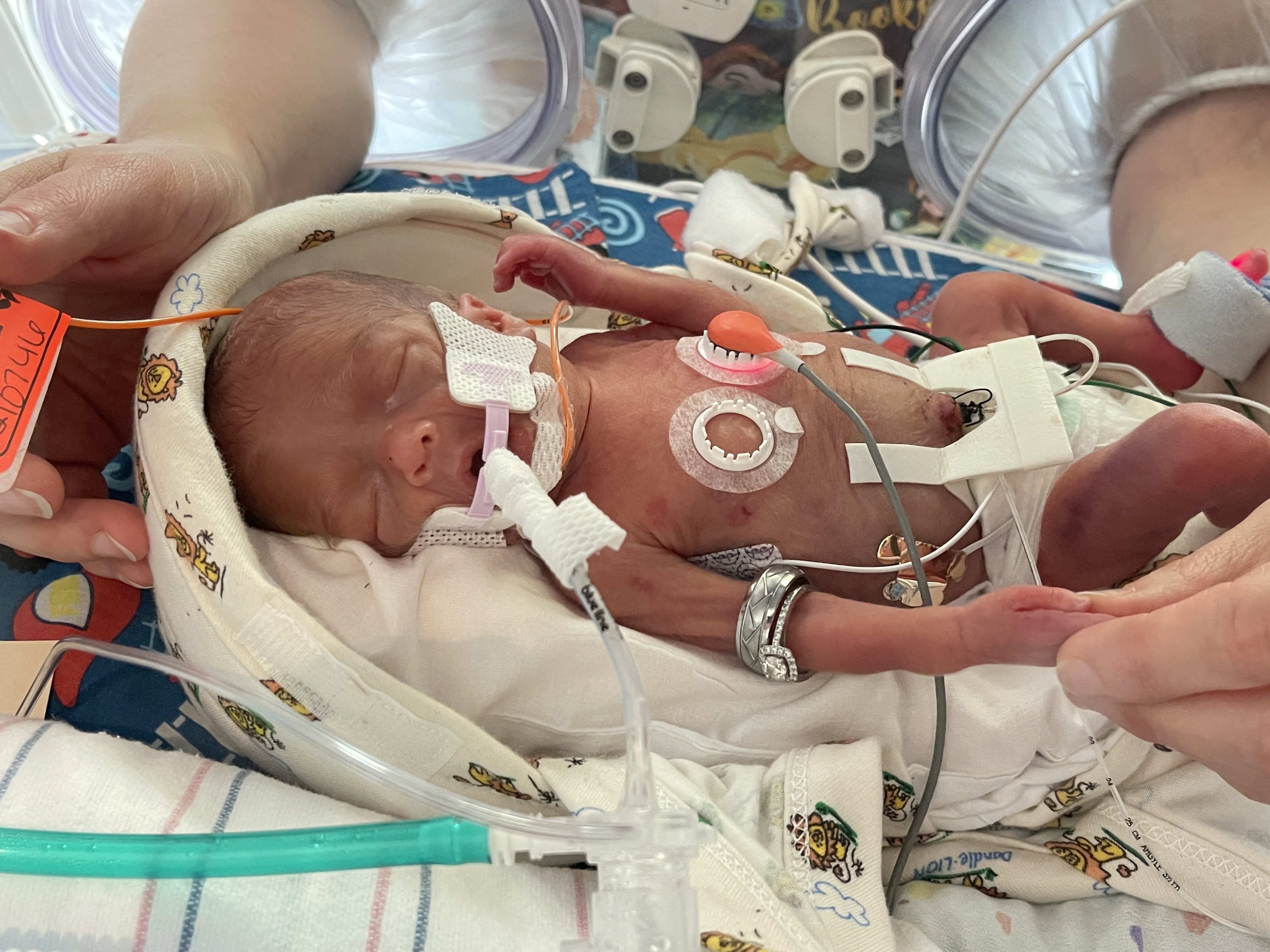
Patient Application
Measurement Sites
Consumables
Sensor Application
Sensor Temperature and Site Time
Workflow
Consideration for Specific Conditions
Edema
Premature Skin
Shunting and Low Perfusion
Hypothermia
Clinical Guides for Transcutaneous Monitoring
Summary
Appendix
Troubleshooting Source of Error
References